Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet–visible spectrophotometry (UV–Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in part of the ultraviolet and the full, adjacent visible spectral regions. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the…
Tag: #Chemistry

Raman Spectroscopy – Legendshub Blog
Raman spectroscopy is an analytical technique where scattered light is used to measure the vibrational energy modes of a sample. It is named after the Indian physicist C. V. Raman who was the first to observe Raman scattering (named after him) in 1928.Raman spectroscopy can provide both chemical and structural information, as well as the identification of substances through their…

Infrared Spectroscopy – Legendshub Blog
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or Vibrational spectroscopy) is the spectroscopy that deals with the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum that is light with a longer wavelength and lower frequency than visible light. It covers a range of techniques, mostly based on absorption spectroscopy. As with all spectroscopic techniques, it can be used to identify and study chemicals. An IR spectrum…
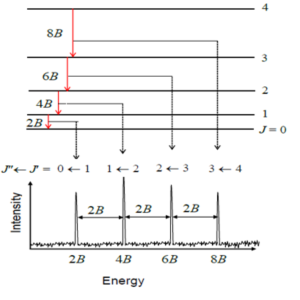
Rotational Spectroscopy – Legendshub Blog
In the previous blog we introduced spectroscopy and its different techniques. In this blog we will discuss Rotational Spectroscopy (also known as Microwave Spectroscopy) in detail. Rotational spectroscopy measures a high-resolution spectrum where the spectral pattern is determined by the three-dimensional structure of the molecule. The quantized energy levels for the spectroscopy come from the overall rotational motion of…

Spectroscopy – Legendshub Blog
There are Millions of chemical compounds everywhere around us. So one question can come in our mind that How can we Identify these compounds? Spectroscopy is the answer of this question. There are a number of spectroscopy techniques by which we can easily know about the structure of the compounds, which elements are present in the compound. In other…

